💻 The Tech Hub
Explore the future of technology
Nicosmos delivers cutting-edge articles, in-depth analyses, and expert insights across hardware, smartphones, gaming, and the digital landscape. Stay informed with content that matters in the ever-evolving world of computing.

Discover Our Tech Coverage
From hardware deep dives to gaming news and marketing trends
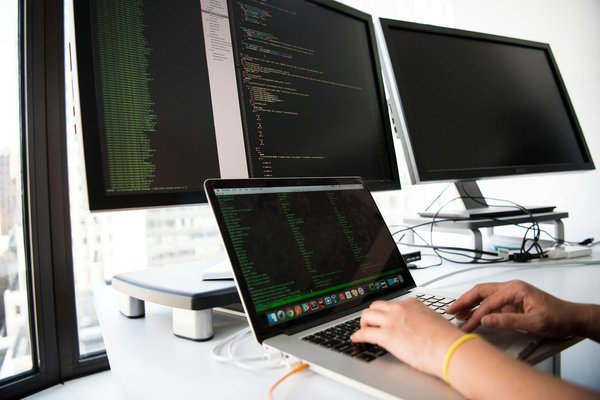

Why Tech Enthusiasts Choose Nicosmos
We bring you comprehensive coverage of everything that shapes the digital world. Our independent editorial approach ensures you get honest perspectives on the technology that impacts your daily life.
- Daily articles covering hardware, smartphones, and gaming
- Detailed benchmark analyses and performance comparisons
- Breaking news from the tech industry worldwide
- Expert guides to help you navigate digital trends
Latest articles
Our recent publications


News
Cazinoul Julius • deutsches Territorium Play & Claim

News
Victimize Of Chafe Bruiser Cassino Fillip · English-language market Enjoy the Game

News
Preferat Servicii Bancare Alternative ◦ piața românească Start Playing

News
Vinn Extra Försök Utan Dröjsmål – nordiska regionen Play Now

News
777 Szektor Befizetés Nélküli Bónusz Meglévő Játékosoknak – HU Claim Your Reward

News
Bote Regreso - región ibérica Enjoy the Game

News
Razkrij Ekskluzivno Spletno Igralnica Nagrade Slovenija Collect Bonus

News
Trükkök Szorzás Keresmény Használat Közben Digitális Játékok Európai Unió Collect Bonus

News
PREMIUM Naročnik Storitev Roberta Williama _ Evropa Collect Bonus

News
Ultimate Joc Cu Roți Plan Pentru Profit Regular} Europa Play Now

News
Comédien Sec INITIALE DEUX CARTES MAIN — République française Commencez Maintenant
News
Comptabilité Inscription Jurer -- marché européen Rejoignez Maintenant

News
Ontdekken Augmented Reality-Spellen Futuristisch · NL Registreer & Win

News
Betdeluxe Aanmeldbonus — Netherlands Registreer Gratis

News
Leger Risico Autoriteiten Staat Voor Staat Netherlands Begin Met Spelen

News
Proberen Afhankelijk Van Het Scherm Vanaf Je Mobiele Apparaat • Benelux Draai Om Te Winnen
News
Richard Kaszinó Befizetés Nélküli Bónusz Hungary Pörgess És Nyerj

Internet
Mastering cybersecurity skills: uncovering ip spoofing tactics
High tech
Storage solutions: Evernex's comprehensive data backup services

hardware
How can you configure a Raspberry Pi 4 for use as a Pi-Hole DNS server to block ads across your entire home network?

High tech
How can you leverage machine learning to optimize logistics in e-commerce?
High tech
What are the best practices for securing sensitive data in AI-driven applications?

High tech
What are the methods to ensure data privacy when using wearable health devices?
Internet
How can you use AWS CloudTrail for logging and monitoring API calls?

Internet
How can you use Jenkins X for Kubernetes-native CI/CD pipelines?
Internet
What are the best practices for handling sensitive data in React applications?

marketing
What are the best practices for digital marketing in UK's nonprofit sector?

marketing
What are the key considerations for developing a GDPR-compliant AI model in the UK?

marketing
What are the steps to create a secure digital identity verification system for UK's online services?

Start Your Tech Journey Today
Dive into our extensive library of articles, reviews, and guides. Whether you're a casual reader or a tech professional, Nicosmos has the content you need to stay ahead of the curve.
Rejoindre →Frequently Asked Questions
What topics does Nicosmos cover?
Nicosmos focuses on seven main categories: hardware, high-tech innovations, internet trends, digital marketing, technology news, smartphones, and video games. We publish daily articles, reviews, and analyses across all these areas to keep you informed about the latest developments in computing and digital technology.
How often is new content published?
We publish fresh content daily, with multiple articles released throughout the week. Our editorial calendar ensures consistent coverage across all categories, from breaking news to in-depth features and comprehensive guides. You'll always find something new when you visit Nicosmos.
Are the reviews and analyses independent?
Absolutely. Nicosmos maintains complete editorial independence. Our writers and contributors provide honest, unbiased perspectives based on thorough research and hands-on experience. We're committed to delivering authentic insights that help readers make informed decisions.
Can I suggest topics for future articles?
Yes! We welcome reader feedback and topic suggestions. While we can't guarantee coverage of every request, we regularly incorporate reader interests into our editorial planning. Feel free to reach out through our contact page with your ideas and questions.
